Playing Cricket with Step-by-Step Instructions for Batting, Bowling, and Fielding
Cricket is a global passion that transcends being just a sport, connecting people from Mumbai’s bustling streets to London’s serene fields. It embodies a rich culture, a way of life, and an exhilarating adventure enjoyed by millions.

History of Cricket
Cricket traces its origins back to the 16th century in England. It has evolved significantly over the centuries and is now one of the most popular sports globally, especially in countries like England, Australia, India, and Pakistan.
Why Learn Cricket?
Cricket not only promotes physical fitness but also fosters teamwork, strategy, and sportsmanship. It’s a versatile game that can be played at various levels, from casual backyard games to professional international matches.
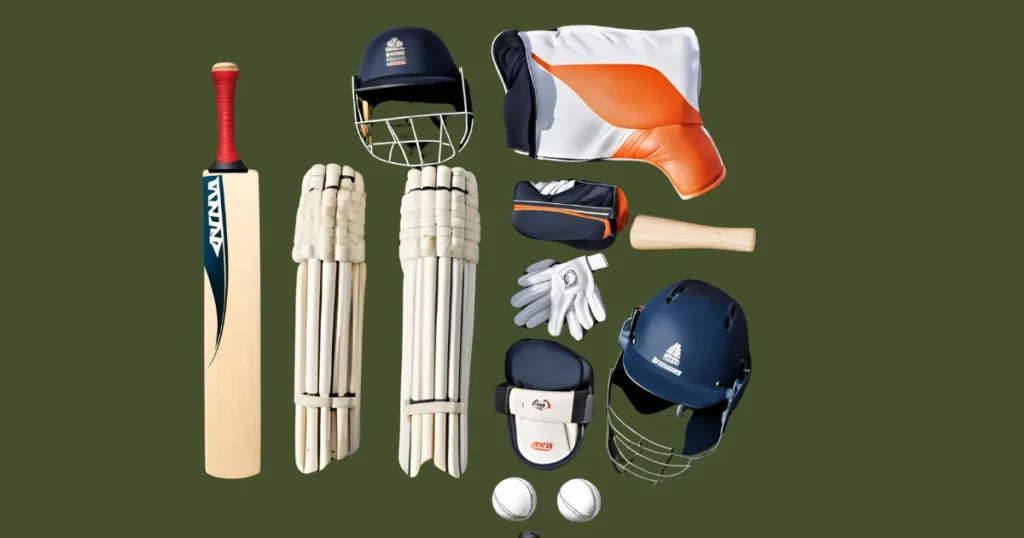
Essential Equipment for Cricket
Before stepping onto the cricket field, it’s crucial to have the right gear. Here’s a list of essential equipment:
1. Cricket Bat
The cricket bat is typically made of willow wood. It has a flat front and a V-shaped back, designed to strike the ball effectively.
2. Cricket Ball
A standard cricket ball is hard and made of cork covered with leather. The ball is either red for traditional test matches or white for limited-overs formats like One Day Internationals (ODIs) and T20s.
3. Protective Gear
- Helmet: Essential for batsmen and wicketkeeper’s to protect the head from fast deliveries.
- Pads: Worn by batsmen and wicketkeepers to protect the legs.
- Gloves: Provide grip and protection for batsmen and wicketkeepers.
- Abdominal Guard: Worn by male players for protection.

4. Clothing
Cricketers typically wear a white or colored kit depending on the format. The clothing includes trousers and a shirt, often accompanied by a jumper in colder conditions.
5. Footwear
Cricket shoes come with spikes to provide traction on the field, which is crucial for both batting and bowling.
6. Additional Accessories
- Wicket-keeping Gloves: Special gloves for the wicketkeeper.
- Thigh Pads and Arm Guards: Provide extra protection for batsmen.
Basic Rules of Cricket
Understanding the basic rules is essential for playing cricket. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
1. The Objective
The primary goal is to score more runs than the opposing team. The team with the most runs at the end of the match wins.
2. Scoring Runs
Runs are scored by hitting the ball with the bat and running to the opposite end of the pitch. Boundaries (balls reaching the fence) score 4 or 6 runs, depending on whether the ball bounced before crossing the boundary.
3. Wickets
A wicket consists of three stumps topped by two bails. A batsman is dismissed when:
4. Innings
Each team bats and bowls once in a limited-overs match, while in test cricket, each team has two innings.
5. Overs
An over consists of six legal deliveries bowled by a single bowler. After an over, a different bowler takes over from the opposite end of the pitch.
6. Match Formats
- Test Matches: Played over five days with each team batting twice.
- ODIs: Each team faces a maximum of 50 overs.
- T20s: Each team faces a maximum of 20 overs.
Understanding the Cricket Field
Field Layout
The cricket field is usually circular or oval, with no fixed dimensions but a diameter ranging between 137 and 150 meters. Key areas include:
Fielding Positions
Fielding positions are strategic spots where players are placed to maximize the chances of getting the batsmen out or stopping runs. Here are some key positions:
| Position | Representation |
|---|---|
| Slip | Catches edges near the wicketkeeper. |
| Gully | Catches deflections. |
| Point | Prevents runs on the off-side. |
| Mid-off | Close to the bowler on the off-side. |
| Mid-on | Close to the bowler on the leg-side. |
| Fine Leg | Near the leg-side boundary. |
| Square Leg | On the leg-side, level with the stumps. |
| Cover | On the off-side, covering drives. |
Roles in a Cricket Team
A cricket team is composed of different players, each with specific roles. Here’s a look at each role:
1. Batsmen
Batsmen score runs by hitting the ball and running between the wickets. They can be:
- Openers: Start the innings and face the new ball.
- Middle Order: Play after the openers, often stabilizing the innings.
- Lower Order: Usually include bowlers who can bat when needed.
READ MORE: Different Ways to Improve Batting Skills.
2. Bowlers
Bowlers aim to dismiss the batsmen by delivering the ball. Types of bowlers include:
- Fast Bowlers: Deliver the ball at high speeds, often above 90 mph.
- Spin Bowlers: Use finger or wrist spin to deceive batsmen.
3. All-Rounders
All-rounders are versatile players who can both bat and bowl effectively. They add balance to the team.
4. Wicketkeeper
The wicketkeeper stands behind the stumps to catch deliveries the batsman misses and to effect run-outs and stumpings.
5. Fielders
Fielders are placed strategically around the field to stop runs and dismiss batsmen. Their positioning is crucial for the team’s defense.
Batting Basics
Batting in cricket involves technique, concentration, and timing. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Grip
2. Stance
3. Backlift
Lift the bat towards the stumps as the bowler runs in. This helps in generating power.
4. Footwork
5. Shots
Defensive Shots
Aggressive Shots
6. Running Between the Wickets
Communication and speed are key. Always call “yes,” “no,” or “wait” to indicate your intention to your partner.
| Shots | Characterization |
|---|---|
| Straight Drive | Hitting straight back past the bowler. |
| Cover Drive | Hitting through the covers on the off-side. |
| Pull Shot | Hitting towards the leg side for a short ball. |
Bowling Basics
Bowling is a critical aspect of cricket. Here’s how to master it:
1. Grip
2. Run-Up
The run-up is the approach to the crease before delivering the ball. Keep it smooth and consistent.
3. Delivery Stride
In the delivery stride, the bowler releases the ball. There are two main types:
4. Types of Deliveries
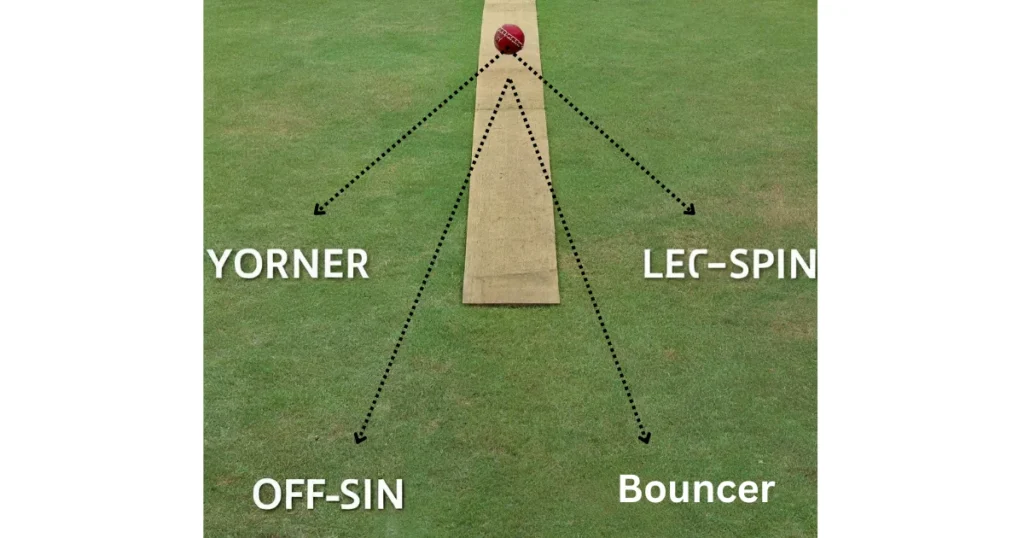
For Fast Bowlers
- Yorker: A full-length delivery aiming at the batsman’s toes.
- Bouncer: A short-pitched delivery aimed at the batsman’s head or chest.
For Spin Bowlers
- Off-Spin: Spins from the off-side to the leg-side for a right-handed batsman.
- Leg-Spin: Spins from the leg-side to the off-side.
5. Field Placement
Field placement varies depending on the type of bowler and the game situation. Common fields include attacking (close-in fielders) and defensive (spread-out fielders).
| Bowling Type | Characterization |
|---|---|
| Fast Bowling | Emphasis on speed, full arm rotation. |
| Spin Bowling | Emphasis on spin, wrist or finger use. |
Fielding Techniques
Fielding is about stopping runs and taking catches. Here’s how to excel:
1. Catching
- High Catches: Cup your hands and watch the ball into your hands.
- Slip Catches: Position your hands together, fingers pointing downwards.
2. Ground Fielding
- Attacking Fielding: Charge the ball and aim to throw it quickly.
- Defensive Fielding: Stay behind the ball, use your body to stop it.
3. Throwing
- Overarm Throw: Used for long distances.
- Underarm Throw: Used for short, quick throws to the wicketkeeper or bowler.
| Technique | Characterization |
|---|---|
| High Catch | Cup hands, watch the ball. |
| Ground Fielding | Charge or stay behind the ball, use body if needed. |
| Overarm Throw | For long-distance throws. |
Tips for Kids and Beginners
Starting cricket can be exciting but also overwhelming. Here are some tips:
1. Start Simple
Begin with basic drills like catching, throwing, and simple batting exercises. Use soft balls to build confidence.
2. Practice Regularly
Consistency is key. Practice different aspects of the game regularly to improve your skills.
3. Play in Groups
Playing with friends or joining a local cricket club helps you learn faster and enjoy the game more.
4. Watch and Learn
Watch cricket matches and videos to understand different techniques and strategies. Observing professionals can be educational and inspirational.
5. Stay Positive
Cricket can be challenging. Focus on enjoying the game and learning from mistakes.
Common Cricket Variations
Cricket has various formats and variations suitable for different contexts:
1. Test Cricket
The longest format, played over five days with unlimited overs and each team batting twice.
2. One Day Internationals (ODIs)
Each team faces a maximum of 50 overs, focusing on scoring quickly.
3. Twenty20 (T20)
A shorter, more explosive format where each team faces a maximum of 20 overs.
4. Street Cricket
Informal cricket played in streets or parks, often with simplified rules and equipment.
5. Indoor Cricket
Played in indoor arenas, this version involves a smaller pitch and often has modified rules.
Play Cricket in Schools
Many schools include cricket in their sports curriculum. Here’s how you can get involved:
1. Join the School Team
Participate in school cricket teams or clubs. This offers structured coaching and regular practice.
2. Attend Cricket Camps
Cricket camps provide intensive training during vacations. They are excellent for skill development.
3. Play in Tournaments
Competing in school tournaments gives you practical experience and improves your game.
4. Learn the Rules
Understanding the rules through lessons or workshops helps you play better and enjoy the game more.
Cricket and Technology
Technology has transformed how cricket is played and followed:
1. Video Analysis
Coaches use video analysis to scrutinize players’ techniques and improve their skills.
2. Darts Technology
Darts technology helps analyze bowling speed, spin, and trajectory, offering insights into improving performance.
3. Cricket Apps
There are numerous apps for tracking scores, following matches, and learning cricket.
4. Online Coaching
Many platforms offer online coaching and tutorials, making learning more accessible.
Give Away
Playing cricket can be incredibly rewarding, whether you are a beginner or a seasoned player. Understanding the game’s rules, mastering the basics of batting and bowling, and practicing regularly are essential steps to becoming proficient.