Natural Remedies for Garden Pests
Introduction:
Maintaining a pest-free garden without relying on harsh chemicals is not only beneficial for the environment but also for the health of your plants and the organisms within your garden ecosystem. In this guide, we’ll explore a variety of natural remedies for controlling garden pests, helping you cultivate a thriving and eco-friendly garden.
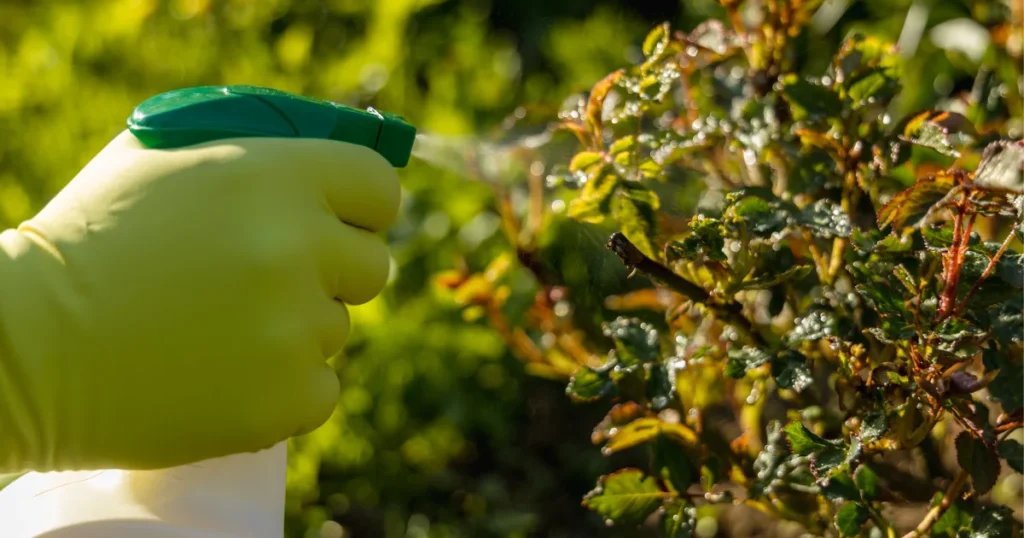

Identifying Common Garden Pests
Garden pests come in various forms, from tiny aphids to voracious caterpillars. Identifying these pests early is crucial for effective pest management and preventing damage to your plants. Learn more about common pest and disease issues in the garden.
Effective Natural Remedies for Pest Control
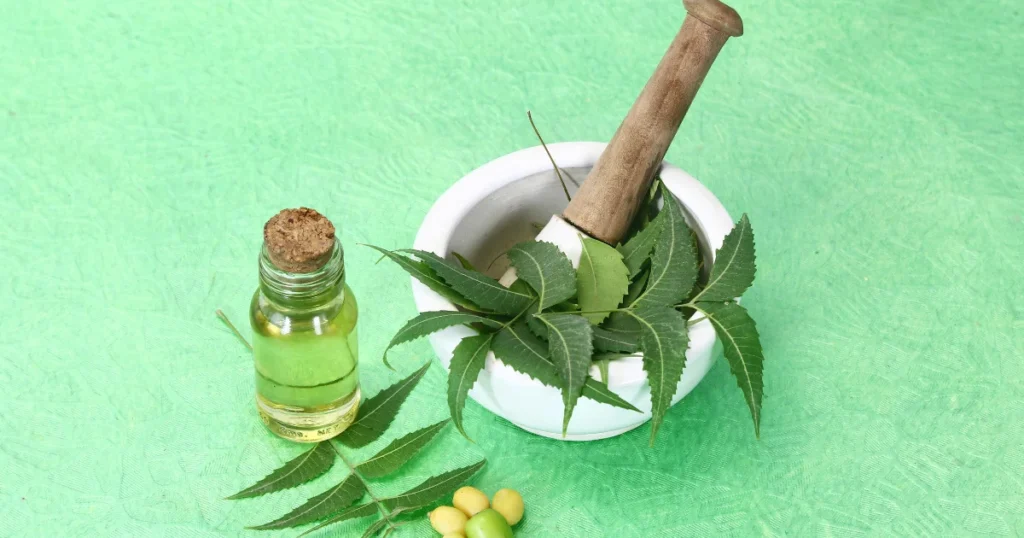
Neem Oil
Neem oil, derived from the seeds of the neem tree, is a natural insecticide that disrupts the growth and development of pests like aphids, whiteflies, and caterpillars. Dilute neem oil in water and spray it on affected plants for effective pest control.

Insecticidal Soap
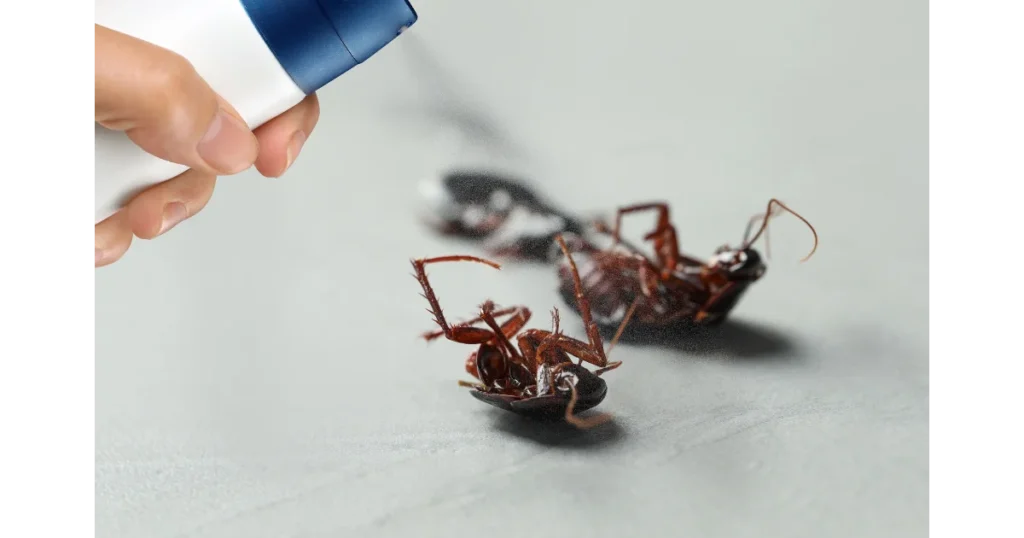

Insecticidal soap, made from potassium salts of fatty acids, works by suffocating soft-bodied pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. Apply a solution of insecticidal soap to affected plants, ensuring thorough coverage of pests.
Garlic Spray
Garlic spray acts as a natural repellent for a wide range of garden pests, including aphids, caterpillars, and beetles. To make garlic spray, blend garlic cloves with water and strain the mixture before spraying it on plants.

Diatomaceous Earth

Diatomaceous earth, a fine powder made from fossilized algae, is effective against crawling insects like ants, slugs, and snails. Sprinkle diatomaceous earth around the base of plants or on the soil surface to create a barrier against pests.
Horticultural Oils
Horticultural oils, such as dormant oil and summer oil, are derived from petroleum or vegetable oils and are effective against a variety of garden pests. These oils smother pests and disrupt their feeding behavior, making them a valuable tool for pest control.

Beneficial Nematodes
Beneficial nematodes are microscopic roundworms that parasitize and kill soil-dwelling pests like grubs, flea larvae, and root maggots. Apply nematodes to the soil according to package instructions to effectively target pest larvae.
Implementing Prevention Strategies
Companion Planting
Companion planting involves growing certain plants together to deter pests or attract beneficial insects. For example, planting marigolds alongside vegetables can repel aphids and nematodes, while attracting pollinators.
Crop Rotation
Rotating crops annually helps disrupt the life cycles of pests and diseases, reducing their buildup in the soil. By alternating plant families in different garden beds each season, you can prevent the recurrence of specific pest problems.
Attracting Beneficial Insects
Encouraging the presence of beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps can help control pest populations naturally. Planting native flowers, providing shelter, and avoiding pesticide use are effective ways to attract beneficial insects to your garden.
Soil Health Maintenance
Maintaining healthy soil through practices like composting, mulching, and avoiding chemical fertilizers helps promote strong plant growth and resilience to pest infestations. Healthy soil also supports beneficial soil microorganisms that contribute to pest control.
Physical Barriers
Physical barriers can prevent pests from accessing your plants and causing damage. Row covers, floating row covers, and netting can be used to protect crops from flying insects, birds, and larger pests like rabbits and deer. Additionally, copper tape can deter slugs and snails by delivering a mild electric shock when they come into contact with it.
Trap Crops
Trap cropping involves planting specific plants that are particularly attractive to pests, diverting them away from your main crops. For example, planting a patch of sacrificial plants like nasturtiums or mustard greens can lure aphids or cabbage worms away from your prized vegetables. After the trap crops become infested, you can remove and dispose of them, reducing pest pressure on your primary crops.
Biological Controls
Biological controls involve using living organisms to control pests. This method includes introducing predators, parasites, or pathogens that target specific pests. For instance, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a bacterial insecticide that targets caterpillars, while predatory nematodes can help control soil-dwelling pests like grubs and root maggots. Integrating biological controls into your pest management strategy can provide long-term, sustainable solutions for garden pest control.
Verdict
Natural remedies offer effective alternatives to chemical pesticides for controlling garden pests while promoting a healthy and sustainable gardening environment. By incorporating these natural pest control methods into your gardening practices and implementing preventative strategies, you can achieve a thriving garden ecosystem teeming with life. Embrace the power of nature in your quest for pest-free gardening and enjoy the bountiful harvests and vibrant blooms that result.






